原型模式指在創建重複對象的同時保持性能。 這種類型的設計模式屬於創建模式,因為此模式提供了創建對象的最佳方法之一。
這個模式涉及實現一個原型介面,它只創建當前對象的克隆。有時直接創建對象時使用這種模式是昂貴的。例如,在昂貴的資料庫操作之後創建對象。因此我們可以緩存對象,在下一個請求時返回其克隆,並在需要時更新資料庫,從而減少資料庫調用。
實現實例
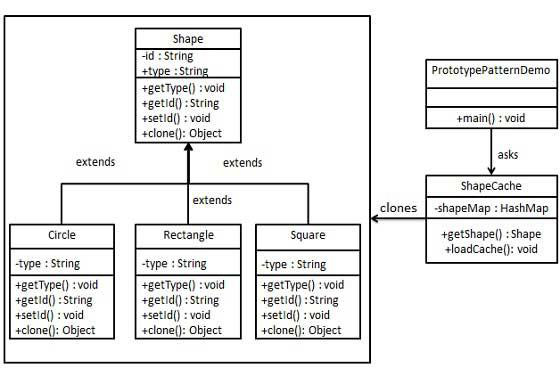
我們將創建一個抽象類Shape和擴展Shape類的具體類。 在下一步中定義ShapeCache類,在Hashtable中存儲形狀(Shape)對象,並在請求時返回其克隆。
PrototypPatternDemo這是一個演示類,將使用ShapeCache類來獲取一個Shape對象。實現結構圖如下所示 -
第1步
創建一個實現Clonable介面的抽象類。
Shape.java
public abstract class Shape implements Cloneable {
private String id;
protected String type;
abstract void draw();
public String getType(){
return type;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public Object clone() {
Object clone = null;
try {
clone = super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return clone;
}
}
第2步
創建擴展上述類的具體類。
Rectangle.java
public class Rectangle extends Shape {
public Rectangle(){
type = "Rectangle";
}
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Inside Rectangle::draw() method.");
}
}
Square.java
public class Square extends Shape {
public Square(){
type = "Square";
}
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Inside Square::draw() method.");
}
}
Circle.java
public class Circle extends Shape {
public Circle(){
type = "Circle";
}
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Inside Circle::draw() method.");
}
}
第3步
創建一個類來獲取具體的類,並將它們存儲在Hashtable中。
ShapeCache.java
import java.util.Hashtable;
public class ShapeCache {
private static Hashtable<String, Shape> shapeMap = new Hashtable<String, Shape>();
public static Shape getShape(String shapeId) {
Shape cachedShape = shapeMap.get(shapeId);
return (Shape) cachedShape.clone();
}
// for each shape run database query and create shape
// shapeMap.put(shapeKey, shape);
// for example, we are adding three shapes
public static void loadCache() {
Circle circle = new Circle();
circle.setId("1");
shapeMap.put(circle.getId(),circle);
Square square = new Square();
square.setId("2");
shapeMap.put(square.getId(),square);
Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle();
rectangle.setId("3");
shapeMap.put(rectangle.getId(), rectangle);
}
}
第4步
PrototypePatternDemo使用ShapeCache類來獲取存儲在Hashtable中的形狀(shape)的克隆。
PrototypePatternDemo.java
public class PrototypePatternDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShapeCache.loadCache();
Shape clonedShape = (Shape) ShapeCache.getShape("1");
System.out.println("Shape : " + clonedShape.getType());
Shape clonedShape2 = (Shape) ShapeCache.getShape("2");
System.out.println("Shape : " + clonedShape2.getType());
Shape clonedShape3 = (Shape) ShapeCache.getShape("3");
System.out.println("Shape : " + clonedShape3.getType());
}
}
第5步
驗證輸出,執行上面的代碼得到以下結果 -
Shape : Circle
Shape : Square
Shape : Rectangle
上一篇:
Java建造者(Builder)模式
下一篇:
Java適配器模式
