在雙向鏈表中每個節點都包含兩個指針,因此與單鏈表相比,在雙鏈表中保存有更多的指針。
將任何元素插入雙向鏈表有兩種情況。 鏈表為空或包含至少一個元素。 執行以下步驟以在雙向鏈表的開頭插入節點。
- 在內存中為新節點分配空間。這將通過使用以下語句來完成。
ptr = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
- 檢查鏈表是否為空。 如果條件
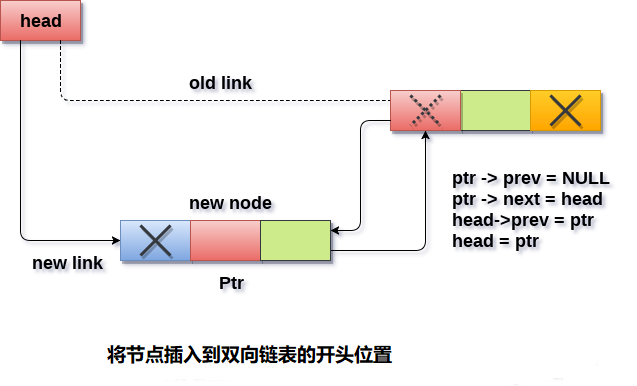
head == NULL成立,則鏈表為空。 在這種情況下,節點將作為鏈表的唯一節點插入,因此節點的prev和next指針將指向NULL,並且頭指針將指向此節點。ptr->next = NULL; ptr->prev=NULL; ptr->data=item; head=ptr; - 在第二種情況下,條件
head == NULL變為false,節點將在開頭插入。 節點的下一個指針將指向節點的現有頭指針。 現有head的prev指針將指向要插入的新節點。這將通過使用以下語句來完成。ptr->next = head; head->prev=ptr;
因為,插入的節點是鏈表的第一個節點,因此它的prev指針指向NULL。 因此,為其前一部分指定null並使頭指向此節點。
ptr->prev = NULL;
head = ptr;
演算法
第1步:IF ptr = NULL
提示 “OVERFLOW” 資訊
轉到第9步
[結束]
第2步:設置 NEW_NODE = ptr
第3步:SET ptr = ptr - > NEXT
第4步:設置 NEW_NODE - > DATA = VAL
第5步:設置 NEW_NODE - > PREV = NULL
第6步:設置 NEW_NODE - > NEXT = START
第7步:SET head - > PREV = NEW_NODE
第8步:SET head = NEW_NODE
第9步:退出
示意圖
C語言實現示例 -
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
void insertbeginning(int);
struct node
{
int data;
struct node *next;
struct node *prev;
};
struct node *head;
void main()
{
int choice, item;
do
{
printf("Enter the item which you want to insert?\n");
scanf("%d", &item);
insertbeginning(item);
printf("Press 0 to insert more ?\n");
scanf("%d", &choice);
} while (choice == 0);
}
void insertbeginning(int item)
{
struct node *ptr = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if (ptr == NULL)
{
printf("OVERFLOW\n");
}
else
{
if (head == NULL)
{
ptr->next = NULL;
ptr->prev = NULL;
ptr->data = item;
head = ptr;
}
else
{
ptr->data = item;
ptr->prev = NULL;
ptr->next = head;
head->prev = ptr;
head = ptr;
}
}
}
執行上面示例代碼,得到以下結果 -
Enter the item which you want to insert?
12
Press 0 to insert more ?
0
Enter the item which you want to insert?
23
Press 0 to insert more ?
2
