指針用於指向存儲在電腦記憶體中任何位置的值的地址。獲取存儲在該位置的值稱為解除引用指針。指針提高了重複過程的性能,例如:
- 遍曆字串
- 查找表
- 控制表
- 樹結構
指針詳細資訊
- 指針算術:指針中有四個算術運算符:
++,--,+,- - 指針數組:可以定義數組以容納多個指針。
- 指針的指針:C語言允許指針的指針等等。
- 將指針傳遞給C語言的函數:通過引用或地址傳遞參數使得被調用函數可以在調用函數中更改傳遞的參數。
- 從C語言函數返回指針:允許函數返回指向局部變數,靜態變數和動態分配記憶體的指針。
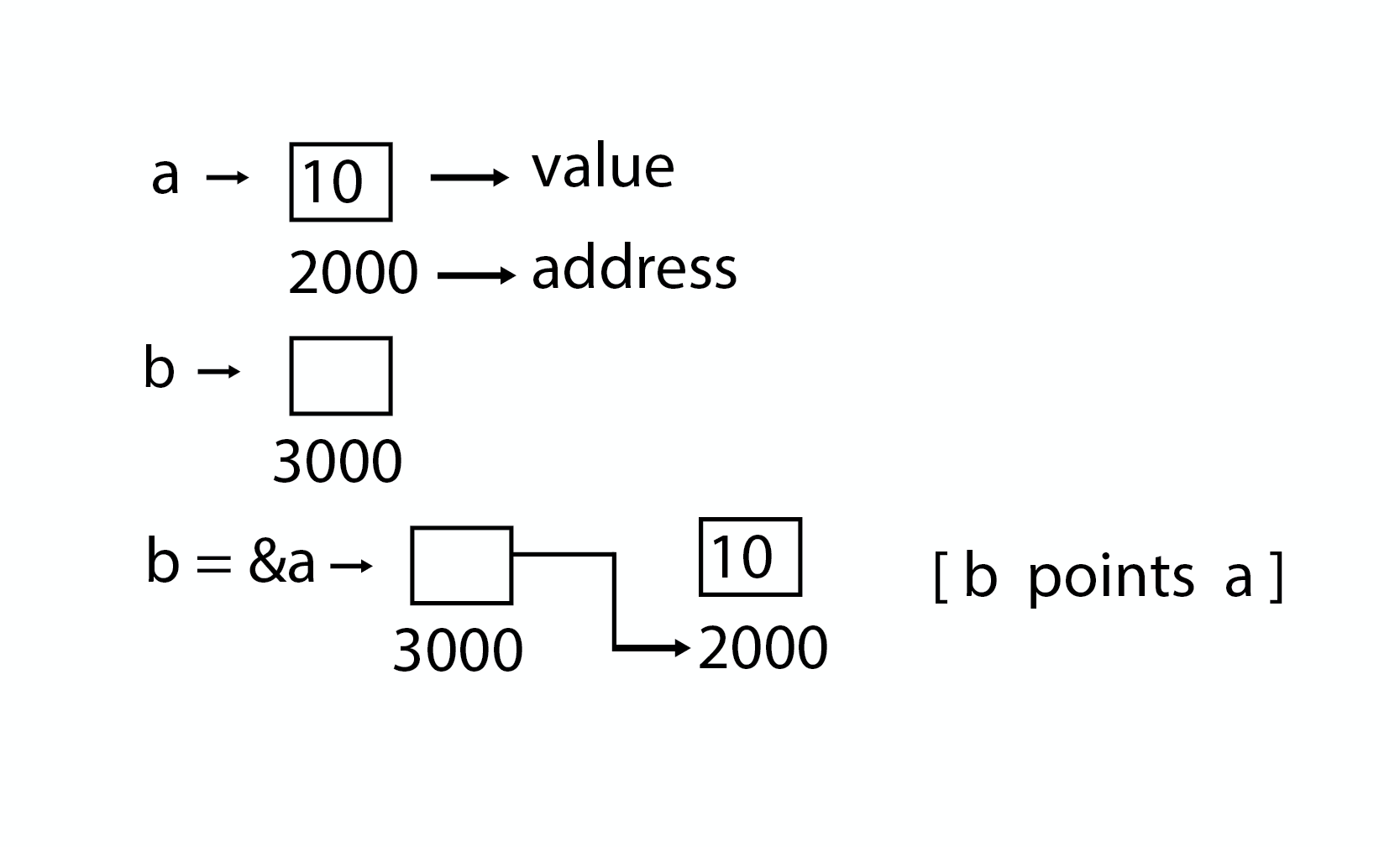
指針示例程式
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 5;
int *b;
b = &a;
printf("value of a = %d\n", a);
printf("value of a = %d\n", *(&a));
printf("value of a = %d\n", *b);
printf("address of a = %u\n", &a);
printf("address of a = %d\n", b);
printf("address of b = %u\n", &b);
printf("value of b = address of a = %u", b);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
執行上面示例代碼,得到以下結果 -
value of a = 5
value of a = 5
value of a = 5
address of a = 13630708
address of a = 13630708
address of b = 13630696
value of b = address of a = 13630708
指針的指針示例程式
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 5;
int *b;
int **c;
b = &a;
c = &b;
printf("value of a = %d\n", a);
printf("value of a = %d\n", *(&a));
printf("value of a = %d\n", *b);
printf("value of a = %d\n", **c);
printf("value of b = address of a = %u\n", b);
printf("value of c = address of b = %u\n", c);
printf("address of a = %u\n", &a);
printf("address of a = %u\n", b);
printf("address of a = %u\n", *c);
printf("address of b = %u\n", &b);
printf("address of b = %u\n", c);
printf("address of c = %u\n", &c);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
執行上面示例代碼,得到以下結果 -
value of a = 5
value of a = 5
value of a = 5
value of a = 5
value of b = address of a = 16252636
value of c = address of b = 16252624
address of a = 16252636
address of a = 16252636
address of a = 16252636
address of b = 16252624
address of b = 16252624
address of c = 16252612
