數組基礎知識
數組是一個容器,該容器可容納固定數目專案,這些專案應該都是相同的類型。大多數的數據結構的利用數組來實現它們的演算法。以下我們來瞭解數組中的概念和一些重要的術語。
-
元素 − 存儲在數組中的每個項被稱為一個元素。
-
索引 − 在一個數組元素所在的每個位置,是具有一個用於識別該元素的數值索引。
數組表示
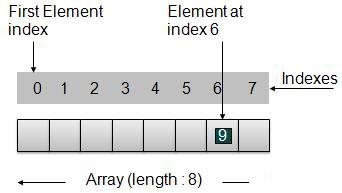
按照如上所示圖中,以下是要考慮的重要問題。
-
索引從 0 開始
-
數組的長度為 8,這意味著它可以存儲 8 個元素。
-
每個元素可以通過它的索引來訪問。例如,我們可以在索引6獲取元素的值:9。
基本操作
以下是由數組所支持的基本操作。
-
遍曆 − 一個一個地列印所有的數組元素。
-
插入 − 給定索引處添加(插入)元素。
-
刪除 − 刪除給定索引處的元素。
-
搜索 − 搜索用特定索引或元素值。
-
更新 − 更新給定索引處的元素。
在C語言中,當初始化一個數組大小,然後將其分配元素的默認值,在下列順序。
| 數據類型 | 默認值 |
|---|---|
| bool | false |
| char | 0 |
| int | 0 |
| float | 0.0 |
| double | 0.0f |
| void | |
| wchar_t | 0 |
插入操作
插入操作是插入一個或多個數據元素到一個數組。根據要求,新元素可以在開始,結束或數組中的任何給定的索引位置加入。
在這裏,可以看到插入操作的實際執行,我們在數組的末尾添加(插入)數據 −
演算法
數組是一個有 MAX 個元素的線性無序數組。
示例
結果
LA是一個線性數組(無序)配有N個元素,K是正整數且 K<= N。 下麵就是 ITEM 插入到 LA 的第 K 個位置的演算法
1. Start 2. Set J = N 3. Set N = N+1 4. Repeat steps 5 and 6 while J >= K 5. Set LA[J+1] = LA[J] 6. Set J = J-1 7. Set LA[K] = ITEM 8. Stop
示例
下麵是上述演算法的執行 −
#include <stdio.h>
main() {
int LA[] = {1,3,5,7,8};
int item = 10, k = 3, n = 5;
int i = 0, j = n;
printf("The original array elements are :\n");
for(i = 0; i<n; i++) {
printf("LA[%d] = %d \n", i, LA[i]);
}
n = n + 1;
while( j >= k){
LA[j+1] = LA[j];
j = j - 1;
}
LA[k] = item;
printf("The array elements after insertion :\n");
for(i = 0; i<n; i++) {
printf("LA[%d] = %d \n", i, LA[i]);
}
}
當編譯和執行,上面的程式產生以下結果 -
The original array elements are : LA[0]=1 LA[1]=3 LA[2]=5 LA[3]=7 LA[4]=8 The array elements after insertion : LA[0]=1 LA[1]=3 LA[2]=5 LA[3]=10 LA[4]=7 LA[5]=8
刪除操作
刪除指從數組中刪除去現有元素,並重新組織數組的所有元素。
演算法
考慮 LA 是一個具有 n 個元素線性數組,以及 K 是正整數,其中 K<= N。下麵的演算法是刪除在 LA 中第 K 個位置的可用元素。
1. Start 2. Set J = K 3. Repeat steps 4 and 5 while J < N 4. Set LA[J-1] = LA[J] 5. Set J = J+1 6. Set N = N-1 7. Stop
示例
下麵是上述演算法的執行 −
#include <stdio.h>
main() {
int LA[] = {1,3,5,7,8};
int k = 3, n = 5;
int i, j;
printf("The original array elements are :\n");
for(i = 0; i<n; i++) {
printf("LA[%d] = %d \n", i, LA[i]);
}
j = k;
while( j < n){
LA[j-1] = LA[j];
j = j + 1;
}
n = n -1;
printf("The array elements after deletion :\n");
for(i = 0; i<n; i++) {
printf("LA[%d] = %d \n", i, LA[i]);
}
}
當編譯和執行,上面的程式產生以下結果 -
The original array elements are : LA[0]=1 LA[1]=3 LA[2]=5 LA[3]=7 LA[4]=8 The array elements after deletion : LA[0]=1 LA[1]=3 LA[2]=7 LA[3]=8
搜索操作
可以在數組元素的值或它的索引執行搜索。
演算法
考慮 LA 是一個具有 n 個元素線性數組,以及 K 是正整數,如 K<= N。下麵的演算法是使用順序搜索找出元素 ITEM 的值。
1. Start 2. Set J = 0 3. Repeat steps 4 and 5 while J < N 4. IF LA[J] is equal ITEM THEN GOTO STEP 6 5. Set J = J +1 6. PRINT J, ITEM 7. Stop
示例
下麵是上述演算法的執行 -
#include <stdio.h>
main() {
int LA[] = {1,3,5,7,8};
int item = 5, n = 5;
int i = 0, j = 0;
printf("The original array elements are :\n");
for(i = 0; i<n; i++) {
printf("LA[%d] = %d \n", i, LA[i]);
}
while( j < n){
if( LA[j] == item ){
break;
}
j = j + 1;
}
printf("Found element %d at position %d\n", item, j+1);
}
當編譯和執行,上面的程式產生以下結果 -
The original array elements are : LA[0]=1 LA[1]=3 LA[2]=5 LA[3]=7 LA[4]=8 Found element 5 at position 3
更新操作
更新操作是從數組指定索引處更新指定的現有元素。
演算法
考慮 LA 是一個具有 n 個元素線性數組,K是正整數,且 K<= N。下麵演算法是更新在 LA 的第K個位置的可用元素。
1. Start 2. Set LA[K-1] = ITEM 3. Stop
示例
下麵是上述演算法的執行
#include <stdio.h>
main() {
int LA[] = {1,3,5,7,8};
int k = 3, n = 5, item = 10;
int i, j;
printf("The original array elements are :\n");
for(i = 0; i<n; i++) {
printf("LA[%d] = %d \n", i, LA[i]);
}
LA[k-1] = item;
printf("The array elements after updation :\n");
for(i = 0; i<n; i++) {
printf("LA[%d] = %d \n", i, LA[i]);
}
}
當編譯和執行,上面的程式產生以下結果
The original array elements are : LA[0]=1 LA[1]=3 LA[2]=5 LA[3]=7 LA[4]=8 The array elements after updation : LA[0]=1 LA[1]=3 LA[2]=10 LA[3]=7 LA[4]=8
