C++語言中的指針是一個變數,它也稱為定位符或指示符,它是指向一個值的地址。
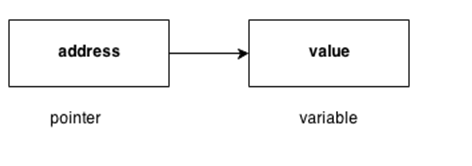
指針的優點
- 指針減少代碼並提高性能,它用於檢索字串,樹等,並與數組,結構和函數一起使用。
- 我們可以使用指針從函數返回多個值。
- 它能夠訪問電腦記憶體中的任何記憶體位置。
指針的使用
在C++語言中有許多指針的使用。
動態記憶體分配
在c語言中,可以使用malloc()和calloc()函數動態分配記憶體,其中使用的就是指針。數組,函數和結構體
C語言中的指針被廣泛用於數組,函數和結構體中。 它減少了代碼並提高了性能。
指針中使用的符號
| 符號 | 名稱 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
& |
地址運算符 | 獲取變數的地址。 |
* |
間接運算符 | 訪問地址的值。 |
聲明指針
C++語言中的指針可以使用*(星號符號)聲明。
int ∗ a; //pointer to int
char ∗ c; //pointer to char
指針示例
下麵來看看看使用指針列印地址和值的簡單例子。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int number=30;
int ∗ p;
p=&number;//stores the address of number variable
cout<<"Address of number variable is:"<<&number<<endl;
cout<<"Address of p variable is:"<<p<<endl;
cout<<"Value of p variable is:"<<*p<<endl;
return 0;
}
執行上面代碼得到如下結果 -
Address of number variable is:0x7ffccc8724c4
Address of p variable is:0x7ffccc8724c4
Value of p variable is:30
在不使用第三個變數的情況下交換2個數字的指針程式示例
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a=20,b=10,∗p1=&a,∗p2=&b;
cout<<"Before swap: ∗p1="<<∗p1<<" ∗p2="<<∗p2<<endl;
∗p1=∗p1+∗p2;
∗p2=∗p1-∗p2;
∗p1=∗p1-∗p2;
cout<<"After swap: ∗p1="<<∗p1<<" ∗p2="<<∗p2<<endl;
return 0;
}
執行上面代碼得到如下結果 -
Address of number variable is:0x7ffccc8724c4
Address of p variable is:0x7ffccc8724c4
Value of p variable is:30
