1- 介绍
本教程文章是基于以下编写的:
- Spring Framework 4.0.4 RELEASE
- Eclipse 4.5 MARS (ok for Eclipse 4.4 LUNA)
在本文中使用Maven来声明Spring库,而不是下载Spring库,并以正常的方式来声明。
Maven是一个工具,可以帮你自动,高效地管理您的库,它已成为惯例,所有 Java 程序员必须知道。如果你不知道如何使用Maven,可以花10分钟就学会如何使用它:
如果你想下载Spring和声明库,您可以用传统的方式见附录在文件的结尾。
2- Spring框架
下图显示了Spring框架的结构。
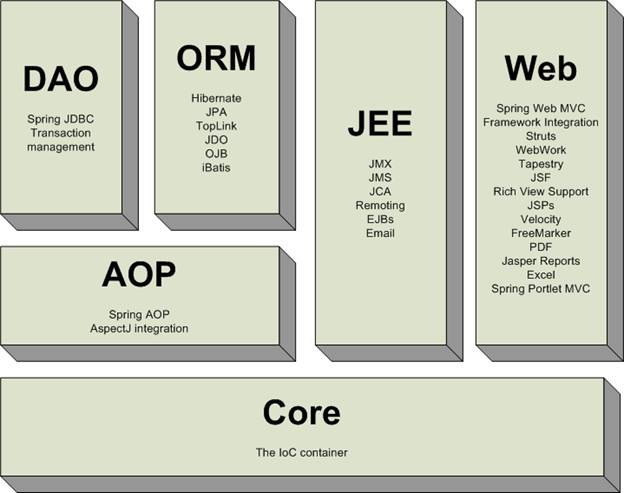

- IoC Container: 这是最重要的,也是最基础的, Spring的基础。它的作用是配置和Java对象的生命周期管理。这篇教程中我们将学习这一部分。
- DAO, ORM, AOP, WEB: 该模块可用于将工具或框架集成到了Spring。
2.1- 反转控制和依赖注入
要了解这个问题,我们使用以下几类:
// Interface HelloWorld
public interface HelloWorld {
public void sayHello();
}
// Class implements HelloWorld
public class SpringHelloWorld implements HelloWorld {
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println("Spring say Hello!");
}
}
// Other class implements HelloWorld
public class StrutsHelloWorld implements HelloWorld {
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println("Struts say Hello!");
}
}
// And Service class
public class HelloWorldService {
// Field type HelloWorld
private HelloWorld helloWorld;
// Constructor HelloWorldService
// It initializes the values for the field 'helloWorld'
public HelloWorldService() {
this.helloWorld = new StrutsHelloWorld();
}
}
显而易见的是 HelloWorldService 类管理创建 HelloWorld 对象。
- 另外,在上述情况下,当 HelloWorldService 对象从它的构造创建时,HelloWorld对象也被创建了。 它是从StrutsHelloWorld 创建。
现在的问题是,您要创建一个HelloWorldService对象,HelloWorld对象也同时被创建,但它必须是SpringHelloWorld。
所以 HelloWorldService 是控制“对象创建” Hello World 的。我们为什么不创建 Hello World 转让由第三方,
而是使用 HelloWorldService ?因为我们有“反转控制”(IOC)的定义。
并且IoC容器将充当管理者角色,创建了HelloWorldService 和 HelloWorld 。
IoC = Inversion of Control
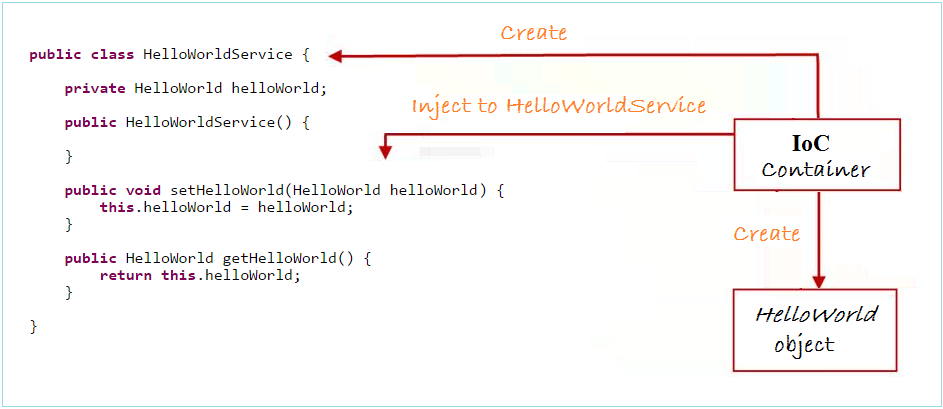
IoC容器创建 HelloWorldService 对象,是通过 setter 方法传递 HelloWorld 对象到HelloWorldService。IoC容器做的是“依赖注入”到HelloWorldService。这里的相关性是指对象之间的依赖关系: HelloWorldService 和 helloWorld.
在这一点上,我们已经明确了什么是 IoC和DI。让我们举个例子来更好的理解。
3- 创建项目
- File/New/Other...

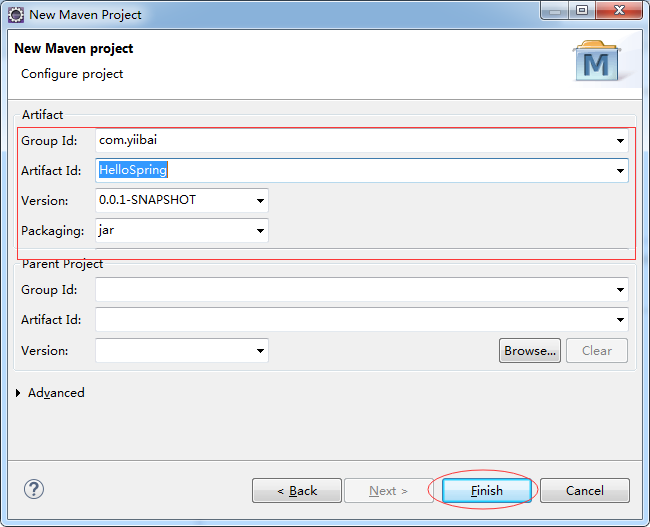
输入:
- Group Id: com.zaixian
- Artifact Id: HelloSpring
您的项目已创建:

确保您的项目是建立在Java7或更高版本。右键单击该项目并选择属性。
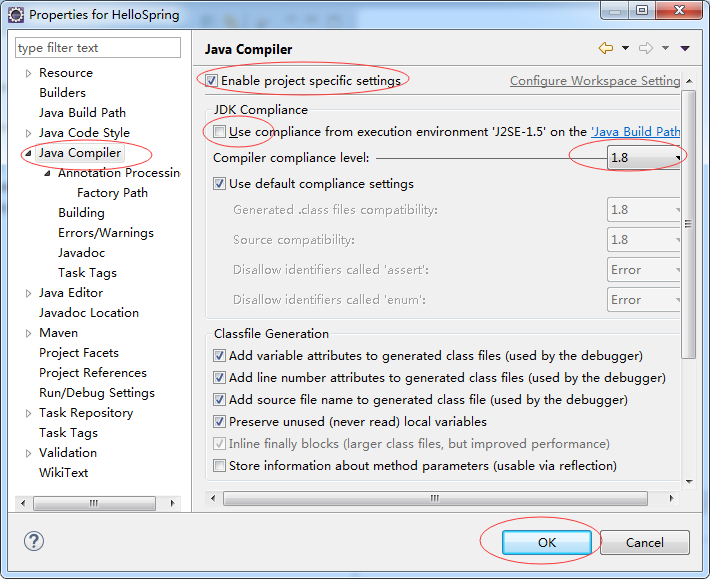
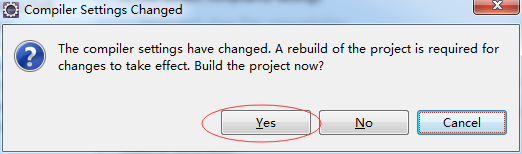


4- 声明Spring的基础库
这是 Spring的 HelloWorld 例子,所以我们只使用基本的Spring库(核心)。打开pom.xml文件来将使用的库声明:
- pom.xml 使用以下内容重新覆盖原上面的内容。
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.zaixian</groupId>
<artifactId>HelloSpring</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<dependencies>
<!-- Spring Core -->
<!-- http://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-core -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
<version>4.1.4.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring Context -->
<!-- http://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-context -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>4.1.4.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
5- 工程代码
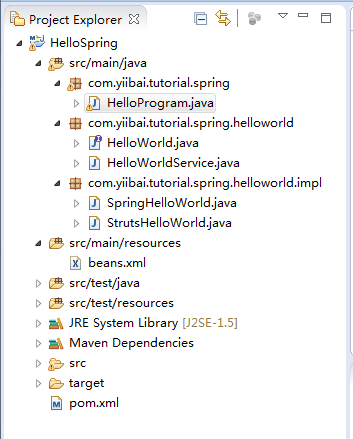
- HelloWorld.java
package com.zaixian.tutorial.spring.helloworld;
public interface HelloWorld {
public void sayHello();
}
- HelloWorldService.java
package com.zaixian.tutorial.spring.helloworld;
public class HelloWorldService {
private HelloWorld helloWorld;
public HelloWorldService() {
}
public void setHelloWorld(HelloWorld helloWorld) {
this.helloWorld = helloWorld;
}
public HelloWorld getHelloWorld() {
return this.helloWorld;
}
}
- SpringHelloWorld.java
package com.zaixian.tutorial.spring.helloworld.impl;
import com.zaixian.tutorial.spring.helloworld.HelloWorld;
public class SpringHelloWorld implements HelloWorld {
@Override
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println("Spring Say Hello!!");
}
}
- StrutsHelloWorld.java
package com.zaixian.tutorial.spring.helloworld.impl;
import com.zaixian.tutorial.spring.helloworld.HelloWorld;
public class StrutsHelloWorld implements HelloWorld {
@Override
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println("Struts Say Hello!!");
}
}
- HelloProgram.java
package com.zaixian.tutorial.spring;
import com.zaixian.tutorial.spring.helloworld.HelloWorld;
import com.zaixian.tutorial.spring.helloworld.HelloWorldService;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class HelloProgram {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
HelloWorldService service =
(HelloWorldService) context.getBean("helloWorldService");
HelloWorld hw= service.getHelloWorld();
hw.sayHello();
}
}
-
beans.xml

<beansxmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<beanid="springHelloWorld"
class="com.zaixian.tutorial.spring.helloworld.impl.SpringHelloWorld"></bean>
<beanid="strutsHelloWorld"
class="com.zaixian.tutorial.spring.helloworld.impl.StrutsHelloWorld"></bean>
<beanid="helloWorldService"
class="com.zaixian.tutorial.spring.helloworld.HelloWorldService">
<propertyname="helloWorld"ref="springHelloWorld"/>
</bean>
</beans>
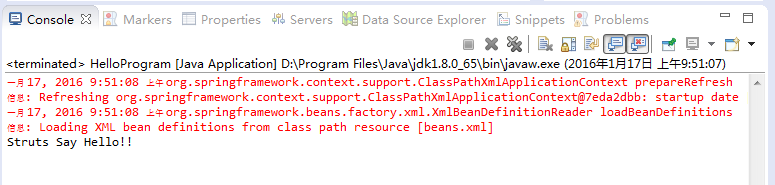
6- 运行示例
运行 HelloProgram.java
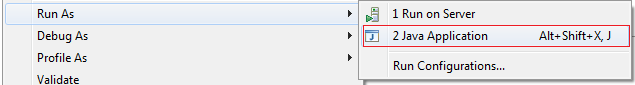
运行 HelloProgram 类的结果如下:


打开 beans.xml 文件并更改配置:
<!-- Original -->
<beanid="helloWorldService"
class="com.zaixian.tutorial.spring.helloworld.HelloWorldService">
<propertyname="helloWorld"ref="springHelloWorld"/>
</bean>
<!-- Change to: -->
<beanid="helloWorldService"
class="com.zaixian.tutorial.spring.helloworld.HelloWorldService">
<propertyname="helloWorld"ref="strutsHelloWorld"/>
</bean>
重新运行 HelloProgram 类并得到以下结果。

7- Spring的工作原理
Spring在这个例子中,工作原理说明如下图所示:
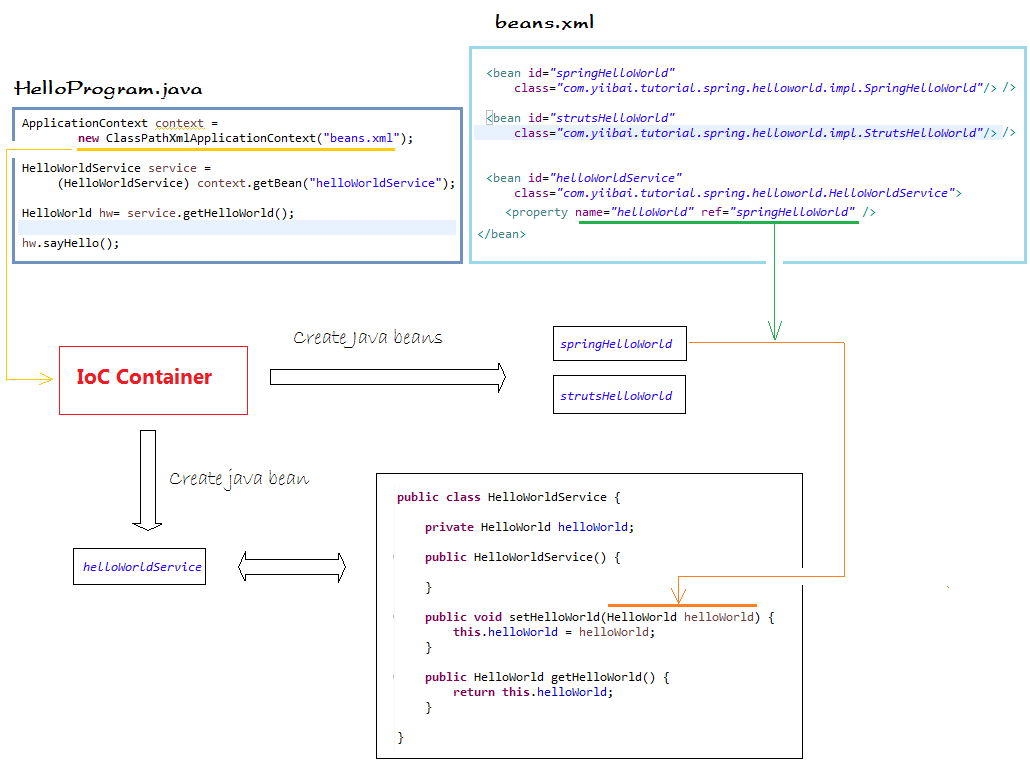

beans.xml
-
这是一个配置文件,您可以在这里声明Java bean。
可以通过读取beans.xml 文件来创建一个应用程序上下文对象
ApplicationContext context =
newClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
在这个例子中,HelloWorldService 是一个 java bean 注入依赖。
<!-- beans.xml -->
<beanid="helloWorldService"
class="com.zaixian.tutorial.spring.helloworld.HelloWorldService">
<!-- Call: helloWorldService.setHelloWorld(springHelloWorld) -->
<propertyname="helloWorld"ref="springHelloWorld"/>
</bean>
8- 使用Spring MVC - 编写Web应用程序
接下来,你可以学习使用Spring MVC编写Web应用程序:
9- 附:下载Spring 库
您可以下载 Spring 从以下网址:
解压下载的zip文件到硬盘驱动器文件夹,如下:
上一篇:
Spring依赖注入servlet会话监听器
下一篇:
安装Spring工具套件到Eclipse
