要在列表中的指定节点之后插入节点,需要跳过所需数量的节点以便到达目标节点,然后根据需要调整指针。
为此,请参考使用以下步骤。
- 为新节点分配内存。 请使用以下语句。
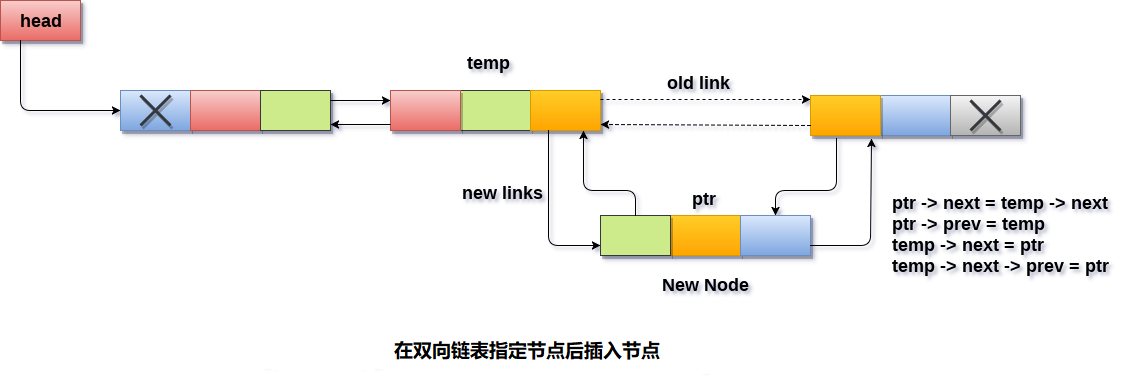
使用指针ptr = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));temp遍历列表以跳过所需数量的节点以到达指定节点。temp=head; for(i=0;i<loc;i++) { temp = temp->next; // the temp will be null if the list doesn't last long up to mentioned location if(temp == NULL) { return; } } temp将指向for循环结束时的指定节点。要在此节点之后插入新节点,因此需要在此处调整ptr指针。使ptr的下一个指针指向temp的下一个节点。ptr -> next = temp -> next;- 使新节点
ptr的prev指针指向temp。
使ptr -> prev = temp;temp指针指向新节点ptr。
使temp -> next = ptr;temp节点的pre指针指向新节点。temp -> next -> prev = ptr;
算法
第1步:IF PTR = NULL
提示:OVERFLOW
转到第15步
[IF结束]
第2步:设置NEW_NODE = PTR
第3步:SET PTR = PTR - > NEXT
第4步:设置NEW_NODE - > DATA = VAL
第5步:SET TEMP = START
第6步:SET I = 0
第7步:重复第8步到第10步直到 I
第8步:SET TEMP = TEMP - > NEXT
第9步:如果TEMP = NULL
第10步:提示 “比所需的元素少”
转到第15步
[结束]
[循环结束]
第11步:设置NEW_NODE - > NEXT = TEMP - > NEXT
第12步:设置NEW_NODE - > PREV = TEMP
第13步:设置TEMP - > NEXT = NEW_NODE
第14步:设置TEMP - > NEXT - > PREV = NEW_NODE
第15步:退出
示意图如下 -
使用C语言实现的示意代码 -
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
void insert_specified(int);
void create(int);
struct node
{
int data;
struct node *next;
struct node *prev;
};
struct node *head;
void main()
{
int choice, item, loc;
do
{
printf("Enter the item which you want to insert?\n");
scanf("%d", &item);
if (head == NULL)
{
create(item);
}
else
{
insert_specified(item);
}
printf("Press 0 to insert more ?\n");
scanf("%d", &choice);
} while (choice == 0);
}
void create(int item)
{
struct node *ptr = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if (ptr == NULL)
{
printf("OVERFLOW");
}
else
{
if (head == NULL)
{
ptr->next = NULL;
ptr->prev = NULL;
ptr->data = item;
head = ptr;
}
else
{
ptr->data = item;printf("Press 0 to insert more ?\n");
ptr->prev = NULL;
ptr->next = head;
head->prev = ptr;
head = ptr;
}
printf("Node Inserted\n");
}
}
void insert_specified(int item)
{
struct node *ptr = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
struct node *temp;
int i, loc;
if (ptr == NULL)
{
printf("OVERFLOW\n");
}
else
{
printf("Enter the location\n");
scanf("%d", &loc);
temp = head;
for (i = 0;i < loc;i++)
{
temp = temp->next;
if (temp == NULL)
{
printf("can't insert\n");
return;
}
}
ptr->data = item;
ptr->next = temp->next;
ptr->prev = temp;
temp->next = ptr;
temp->next->prev = ptr;
printf("Node Inserted\n");
}
}
执行上面示例代码,得到以下结果 -
Enter the item which you want to insert?
12
Node Inserted
Press 0 to insert more ?
0
Enter the item which you want to insert?
90
Node Inserted
Press 0 to insert more ?
2
