二叉搜索树的简介:
- 二叉搜索树它是二叉树的一种类别,其节点按特定顺序排列。这也称为有序二叉树。
- 在二叉搜索树中,左子树中所有节点的值小于根的值。
- 类似地,右子树中所有节点的值大于或等于根的值。
- 此规则将递归地应用于根的所有左子树和右子树。
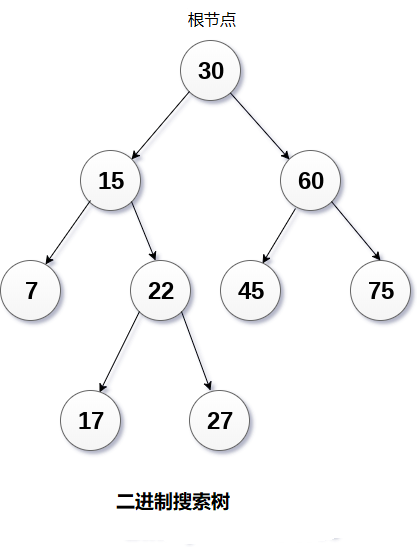
二叉搜索树如上图所示。在二叉搜索树上应用的约束,可以看到根节点30在其左子树中不包含任何大于或等于30的值,并且在其右子树中也不包含任何小于30的值的子树节点值。
使用二叉搜索树的优点
搜索在二叉搜索树中变得非常有效,因为得到每个步骤的提示,哪个子树包含所需元素。
与数组和链表相比,二叉搜索树被认为是有效的数据结构。 在搜索过程中,它会在每一步删除半个子树。 在二叉搜索树中搜索元素需要o(log2n)时间。 在最坏的情况下,搜索元素所花费的时间是0(n)。
与数组和链表中的操作相比,它还加快了插入和删除操作。
问题: 如何使用以下数据元素创建二叉搜索树。
43, 10, 79, 90, 12, 54, 11, 9, 50
- 首先,将
43插入树中并作为树的根。 - 读取下一个元素,如果它小于根节点元素,则将其作为左子树的根插入。
- 否则,将其作为右子树的根插入。
使用给定元素创建二叉搜索树的过程如下图所示。

二叉搜索树的操作
在二叉搜索树上可以执行许多操作。如下表所示 -
| 编号 | 操作 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 在二叉搜索树中搜索 | 在二叉搜索树中查找某些特定元素的位置。 |
| 2 | 在二叉搜索树中插入 | 在适当的位置向二叉搜索树添加新元素,以便BST的属性不会违反。 |
| 3 | 在二叉搜索树中删除 | 从二叉搜索树中删除某个特定节点。 然而,根据节点具有的子节点数,可以存在各种删除情况。 |
二叉搜索树的C语言实现代码
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
Node *left;
Node *right;
};
Node* create(int item)
{
Node* node = new Node;
node->data = item;
node->left = node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
void inorder(Node *root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
inorder(root->left);
cout<< root->data << " ";
inorder(root->right);
}
Node* findMinimum(Node* cur)
{
while(cur->left != NULL) {
cur = cur->left;
}
return cur;
}
Node* insertion(Node* root, int item)
{
if (root == NULL)
return create(item);
if (item < root->data)
root->left = insertion(root->left, item);
else
root->right = insertion(root->right, item);
return root;
}
void search(Node* &cur, int item, Node* &parent)
{
while (cur != NULL && cur->data != item)
{
parent = cur;
if (item < cur->data)
cur = cur->left;
else
cur = cur->right;
}
}
void deletion(Node*& root, int item)
{
Node* parent = NULL;
Node* cur = root;
search(cur, item, parent);
if (cur == NULL)
return;
if (cur->left == NULL && cur->right == NULL)
{
if (cur != root)
{
if (parent->left == cur)
parent->left = NULL;
else
parent->right = NULL;
}
else
root = NULL;
free(cur);
}
else if (cur->left && cur->right)
{
Node* succ = findMinimum(cur- >right);
int val = succ->data;
deletion(root, succ->data);
cur->data = val;
}
else
{
Node* child = (cur->left)? Cur- >left: cur->right;
if (cur != root)
{
if (cur == parent->left)
parent->left = child;
else
parent->right = child;
}
else
root = child;
free(cur);
}
}
int main()
{
Node* root = NULL;
int keys[8];
for(int i=0;i<8;i++)
{
cout << "Enter value to be inserted";
cin>>keys[i];
root = insertion(root, keys[i]);
}
inorder(root);
cout<<"\n";
deletion(root, 10);
inorder(root);
return 0;
}
执行上面示例代码,得到以下结果:
Enter value to be inserted? 10
Enter value to be inserted? 20
Enter value to be inserted? 30
Enter value to be inserted? 40
Enter value to be inserted? 5
Enter value to be inserted? 25
Enter value to be inserted? 15
Enter value to be inserted? 5
5 5 10 15 20 25 30 40
5 5 15 20 25 30 40
上一篇:
二叉树
下一篇:
平衡搜索树(AVL树)
